반응형

1926번: 그림
어떤 큰 도화지에 그림이 그려져 있을 때, 그 그림의 개수와, 그 그림 중 넓이가 가장 넓은 것의 넓이를 출력하여라. 단, 그림이라는 것은 1로 연결된 것을 한 그림이라고 정의하자. 가로나 세로
www.acmicpc.net
전형적인 그래프 탐색 문제이며 단계별로 풀어보기에서
DFS와 BFS단계 문제를 풀어보면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
총 그림의 개수와 가장 넓은 그림의 넓이를 저장할 변수를 만들고
DFS나 BFS를 실행 할 때마다 그림의 개수를 세고, 그림의 넓이를 센다.
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 500
int map[MAX][MAX];
bool visit[MAX][MAX];
int N, M;
int cnt = 0;
int total = 0;
int result = 0;
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
//DFS
void dfs(int x, int y) {
visit[x][y] = true;
cnt++;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx >= 0 && nx < N && ny >= 0 && ny < M) {
if(visit[nx][ny] == false && map[nx][ny] == 1) {
dfs(nx, ny);
}
}
}
}
//BFS
void bfs(int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({x, y});
visit[x][y] = true;
cnt = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().first;
int y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx >= 0 && nx < N && ny >= 0 && ny < M) {
if(visit[nx][ny] == false && map[nx][ny] == 1) {
q.push({nx, ny});
visit[nx][ny] = true;
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 1 && visit[i][j] == false) {
cnt = 0;
bfs(i, j);
total++;
result = cnt > result ? cnt : result;
}
}
}
cout << total << endl << result << endl;
return 0;
}
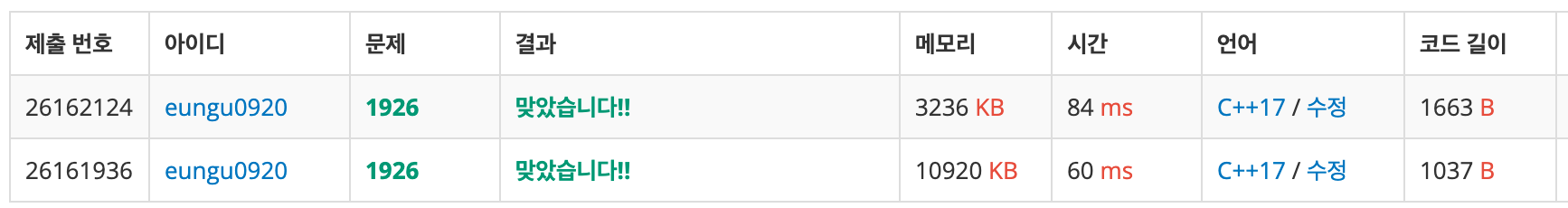
위에가 BFS를 사용해 채점한 것이고
아래가 DFS를 사용해 채점한 것이다.
시간은 BFS가 더 걸렸지만 메모리 사용에 있어 덜 사용했다.
반응형
'BaekJoon > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7569 : 토마토 (C++) (0) | 2021.02.08 |
|---|---|
| 1697 : 숨바꼭질 (C++) (0) | 2021.02.08 |
| 2576 : 홀수 (C++) (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| 2583 : 영역 구하기 (C++) (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| 1946 : 신입 사원 (C++) (0) | 2021.02.05 |




댓글